In order to have a healthy body, balanced nutrition is very important. In addition to proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, water, and minerals, dietary fiber, ranked “the seventh nutrient,” is also one of the essential nutrients needed by the human body.
1. What is dietary fiber?
Dietary fiber is defined as a polymer with a degree of polymerization ≥3, naturally present in plants, extracted from plants, or directly synthesized from plants. It is edible, indigestible and unabsorbable by the human small intestine, and represents a meaningful carbohydrate polymer for human health.
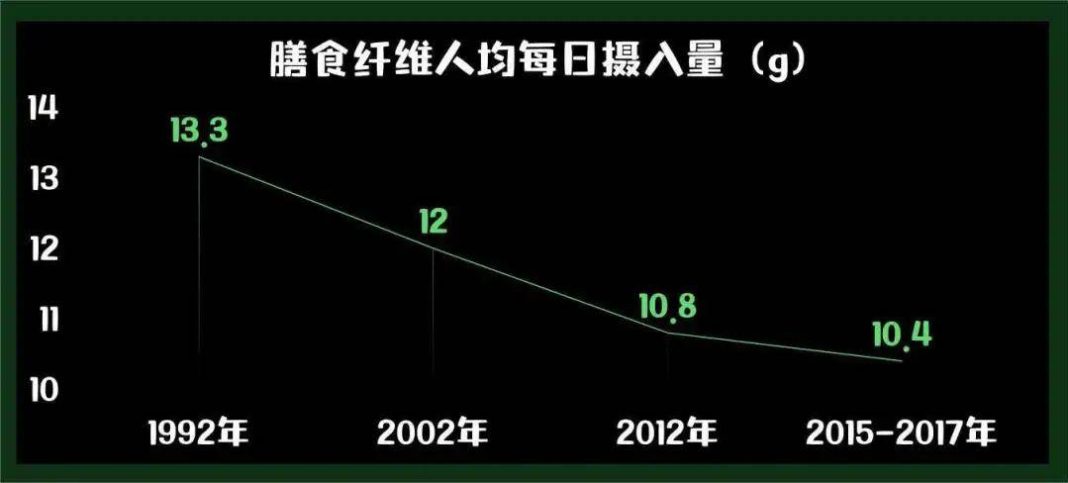
Since 1992, the intake of dietary fiber by residents in our country has been continuously declining [13]…
What problems arise from insufficient dietary fiber intake?
A short-term lack of dietary fiber intake may lead to constipation, while long-term inadequate intake indicates structural issues in the overall diet, potentially increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, and intestinal disorders.
Targeting modern health concerns precisely, sufficient dietary fiber intake can:
1. Increase satiety, with its intake levels being inversely related to BMI, body fat percentage, and weight.
2. Increase stool volume, promote bowel movements, and prevent constipation.
3. Positively regulate fasting and/or postprandial blood sugar, enhance insulin sensitivity, and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
4. Help reduce total blood cholesterol or low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels.
5. Potentially increase the number or vitality of beneficial intestinal bacteria, some of which produce short-chain fatty acids after fermentation by gut flora, a crucial component in maintaining intestinal health.
6. Assist in lowering the risk of colon cancer. [1-11]
Many modern individuals encounter some degree of trouble in these aspects, but that’s okay because dietary fiber is here to help.
The recommended daily intake of dietary fiber for different age groups is as follows (China Dietary Reference Intakes for Residents (2023 Edition):
The beneficial effects of dietary fiber on the human body are mainly related to dietary structure and total caloric intake. In China, the recommendation is to ingest 8-12g of dietary fiber for every 1000 kcal of energy consumed, mainly sourced from natural foods.
Whole grain gentleman reminds you: natural foods contain a variety of dietary fiber types with complex structures. One type of food usually contains multiple dietary fibers, with diverse physiological effects and ample accumulated health evidence over time.
However, extracted, purified, or even artificially synthesized dietary fiber differs – with a simpler structure, it may not provide as comprehensive health benefits as natural foods. It should be approached differently.