Our country is facing the issue of an aging population,
and the aging process is accelerating.
By the end of 2022,
the number of elderly people aged 65 and above in our country
will reach nearly 210 million,
with two-thirds of them living in a
state of multiple chronic conditions.
The health of the elderly in our country urgently needs attention.
As individuals age, their physical and mental functions will gradually decline to varying degrees, leading to malnutrition issues. Additionally, the presence of multiple chronic diseases in the elderly can result in insufficient nutrient intake and muscle loss, increasing the risk of illness.
Common nutritional problems in the elderly
1. Chewing difficulties:
One of the reasons for weight loss in the elderly is poor oral health, such as poorly fitted dentures, missing teeth, oral ulcers, swollen gums, etc.
2. Constipation or diarrhea:
Due to decreased digestive function, slowed gastrointestinal motility, reduced beneficial gut bacteria, inadequate intake of fiber-rich foods, the elderly may experience indigestion or constipation. Some elderly individuals may also experience diarrhea or constipation due to lactose intolerance or a monotonous diet.
3. Osteoporosis:
Reduced outdoor activities, inadequate exposure to sunlight leading to vitamin D deficiency, combined with a monotonous diet low in protein and calcium without timely supplementation, can contribute to osteoporosis. Long-term use of glucocorticoids, immunosuppressants, anti-tumor drugs, etc., can also cause osteoporosis.
4. Sarcopenia:
Sarcopenia is influenced not only by age and primary aging factors but also by nutritional status (inadequate energy and protein intake, gastrointestinal disturbances), disease status (organ failure, neurodegenerative changes, inflammation or endocrine disorders, malignant tumors, etc.), and activity levels (bedridden, prolonged sitting, limb dysfunction, etc.).
What to do about malnutrition in the elderly?
Should elderly individuals eat more hearty meals or keep it light?
Is it better for the elderly to be a little overweight or lean?
How to ensure the nutrition of elderly friends?
Nutritional Information:
In July 2017, the State Council issued the “National Nutrition Plan (2017-2030).” The plan mentions the importance of conducting economic research on nutrition and health, nutrition and social development. One of the primary actions of the National Nutrition Plan is to improve the nutritional status of the elderly population through various measures to meet their nutritional needs.
Department of Nutrition, Hainan Hospital, People’s Liberation Army General Hospital
Provides a
Dietary Guidelines for the Elderly Aged 65-79
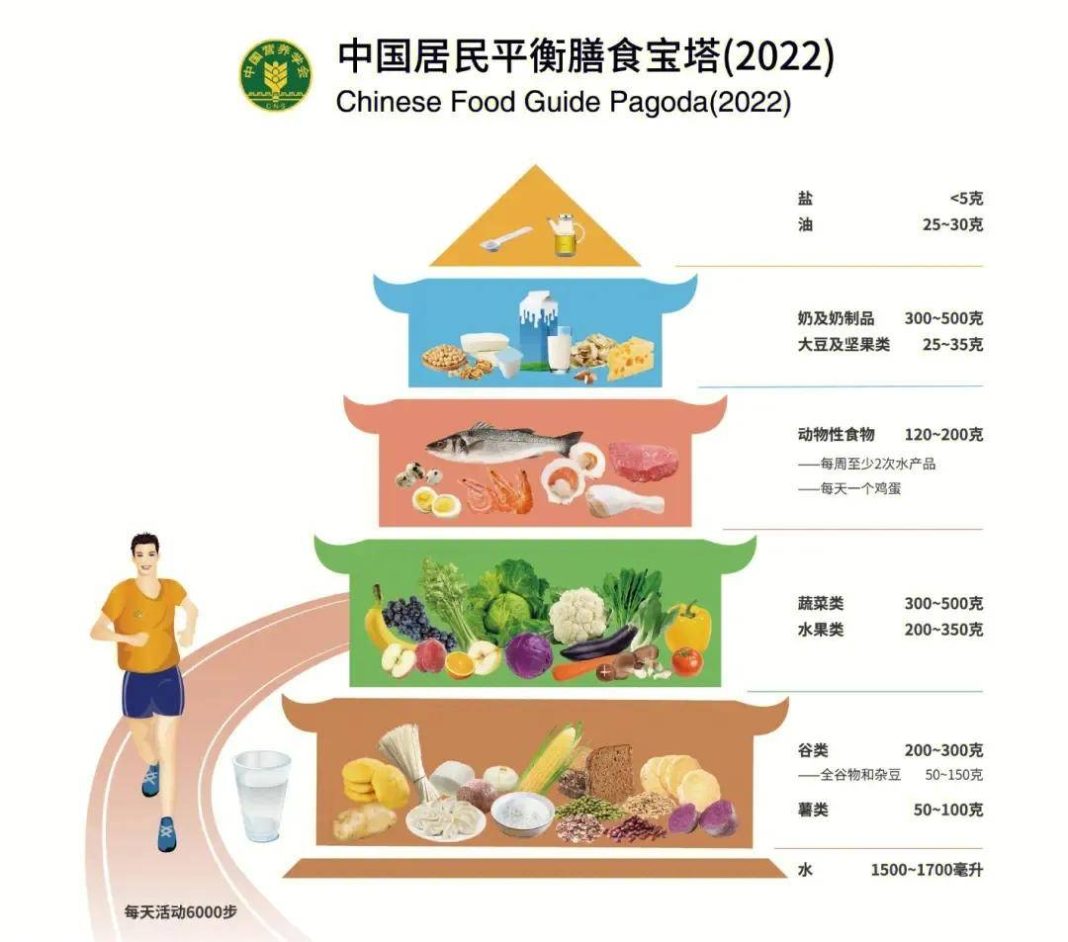
Opt for a variety of foods and maintain a diverse diet
When choosing staple foods, in addition to common choices like rice, steamed buns, noodles, and mantou, consider whole grains such as millet, corn, oats, quinoa, as well as tubers like potatoes, sweet potatoes, and yams;
Consume 4-5 types of vegetables and fruits daily, with smaller portions and greater variety; vary your consumption of animal products, including seafood, poultry, and livestock;
Consume different types of dairy and bean products, such as milk, powdered milk, yogurt, cheese, soy milk, tofu, dried tofu, etc.
Eat together to maintain a good appetite
Encourage the elderly to select, prepare, taste, and critique food together with family members. Solitary or empty-nest elderly individuals can participate in communal dining at elderly dining tables or community canteens;
Use various cooking methods to enhance the color and flavor of food, increasing its appeal and making cooking a part of the elderly lifestyle.
Engage in outdoor activities to delay muscle atrophy
Reduce sedentary time and actively engage in outdoor activities such as walking, brisk walking, calisthenics, leg lifts while sitting, upper limb stretching exercises, Tai Chi, etc.;
Many say, “A high price for thinness in old age,” but this is actually a misconception. Being too thin is not suitable for the elderly as it can reduce the body’s disease resistance, increase the risk of malnutrition. It is recommended for elderly individuals to maintain a BMI between 20-26.9 kg/m2;
Consume 50g of meat per day, 50-100g of fish, shrimp, or poultry; and include dairy in your daily diet, as the whey protein in milk can promote muscle synthesis and prevent muscle atrophy.
Undergo regular health checks to assess nutritional status
It is advisable for elderly individuals to undergo health check-ups 1-2 times a year, monitor their weight regularly, and have assessments of body composition;
Regularly visit the Department of Nutrition for nutritional risk screening and assessment, and receive personalized nutrition management.
Good nutritional status and a balanced diet
play a key role in preventing malnutrition in the elderly.
Wishing every elderly person a life of peace, health, and joy.