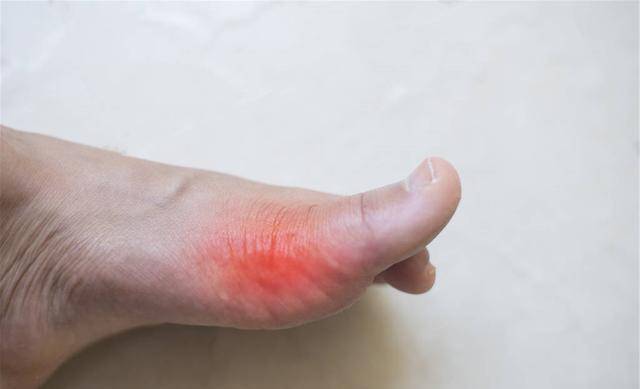
Gout is a common disease, many people fail to control excessive uric acid levels in the body in a timely manner, leading to a buildup of urate salts which can cause joint damage and may trigger gout. In order to effectively improve the condition, medication should be taken promptly, and the correct principles must be followed during medication to maintain stable uric acid levels. Otherwise, gout can worsen and cause bodily harm.
1. Anti-inflammatory drugs should not be used frequently.
Those experiencing gout should use medication correctly and avoid prolonged use of some anti-inflammatory drugs. Many people may feel localized pain during acute attacks and extended use of pain relievers may have side effects, even affecting the function of other vital organs, causing varying degrees of liver and kidney damage.
Therefore, during acute attacks, dietary control is recommended, along with the use of uric acid-lowering medications to improve the condition. Avoid using pain relievers to alleviate localized pain as long-term dependency may lead to side effects.
2. Do not stop medication blindly.
Gout patients should not stop medication as soon as the condition stabilizes. Many individuals do not follow medical advice and discontinue medication once they notice a decrease in uric acid concentration, which may result in a continued increase in uric acid levels and recurrence of the condition.
Gout is not a disease that can be improved in a short time. Patients need to patiently adhere to medication under a doctor’s guidance. Halting medication at the first sign of decreased uric acid concentration may cause a rebound increase in uric acid levels, leading to continued gout progression and bodily harm.
3. Avoid certain foods during medication.
Gout is mainly related to disorders in purine metabolism, and dietary restrictions are necessary to improve the condition. If uric acid-lowering medications are being taken to control the disease progression, but dietary guidelines are not followed, excessive intake of high-purine foods may result in increased uric acid production, leading to disease recurrence or reducing the effectiveness of the medication.
4. Avoid overusing antibiotics.
Gout patients should avoid excessive use of antibiotics during medication. Many individuals, upon experiencing acute gout attacks with localized joint damage and inflammation, tend to indiscriminately use large amounts of antibiotics. However, antibiotics are not very effective in treating acute gout attacks and may even worsen the condition.
Most medications are excreted from the body via the kidneys. Overusing antibiotics can impair kidney function, affecting the excretion of uric acid, and making the pain more pronounced. Therefore, antibiotics should not be overused.
5. Seek treatment early.
Long-term use of uric acid-lowering medications also carries risks, as most of these medications need to be excreted by the kidneys through increased urine output, thereby reducing uric acid levels.
However, if kidney function is already impaired, prolonged medication use will further strain the kidneys, worsening the damage to kidney function and reducing the effectiveness of uric acid-lowering medications. Hence, it is crucial to seek treatment early for this disease and not wait until kidney function is impaired before starting medication.