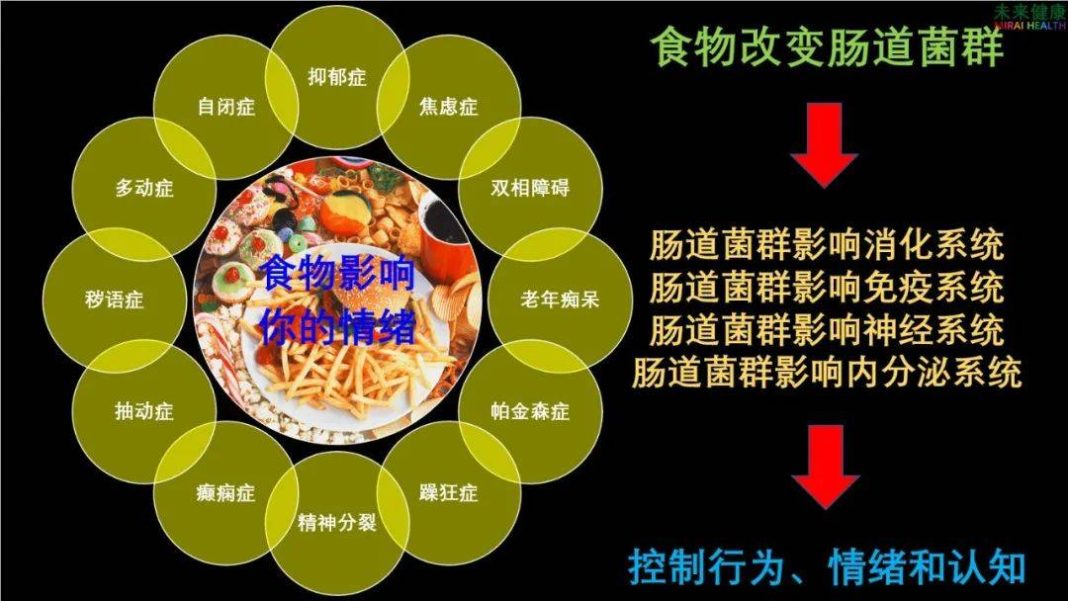
The Food and Mind Laboratory discovered nearly 20 years ago that abnormal gut microbiota and gut-brain axis dysfunction are the main causes of psychological and neurological issues such as depression. Regardless of the treatment method, restoring gut microbiota through dietary adjustments and enhancing gut-brain axis function is essential and the simplest, most cost-effective step to improve health. Therefore, Food and Mind emphasizes the critical role of diet in psychological and brain health, advocating for improving emotions and cognition through healthy eating for a happier life. (Is depression a psychological or physiological illness?)
The purpose of establishing Food and Mind is to organize and introduce our research and findings in a series, allowing more people to eliminate mental illnesses, increase happiness, and improve health through the most cost-effective and easy-to-implement correct dietary methods. By promoting psychological and brain health through healthy eating (“from food to mood”), this is also the reason for the naming of Food and Mind.
There is an increasing amount of research worldwide that supports the viewpoint of Food and Mind. In just 5 years, the searches related to food and mood have increased a hundredfold, reaching over a billion entries. A large-scale tracking study published on July 3, 2024 (tracking over 180,000 people for 11.6 years) revealed that there is a linear relationship between diet quality and the risk of depression, anxiety, and comorbid depression-anxiety. For each 100-point increase in diet quality score (based on the Lancet diet index), the risk of depression decreases by 13.6%, anxiety by 15.8%, and the risk of both depression and anxiety occurring simultaneously decreases by 16.8%. (Adherence to the EAT-lancet diet and incident depression and anxiety – PMC)
A meta-analysis from 2022 (involving over 150,000 participants) found a significant correlation between dietary inflammatory index and psychological state, with this association being more pronounced in women. Compared to the pro-inflammatory diet group, the anti-inflammatory diet group experienced a 45% reduction in the risk of depression (49% in women, 27% in men) and a 66% reduction in the risk of anxiety (80% in women, 47% in men). (Dietary inflammatory potential and the incidence of depression and anxiety: a meta-analysis – PMC)
The inflammatory index of the diet can be calculated based on the pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory effects of different foods in the diet and is currently one of the most commonly used indicators of diet quality. For more information, refer to a healthy breakfast for a week (71) – What kind of diet promotes inflammation.
—
Continued in the next message…