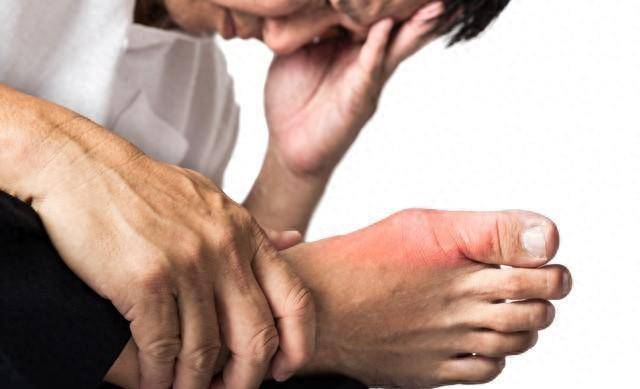
Gout, a type of arthritis inflammation caused by abnormal purine metabolism in the body, often quietly flares up due to a big meal or a gathering. Imagine waking up on a sunny morning, ready to embrace a new day, but suddenly, your toe is intensely painful, as if thousands of needles are piercing it, making even walking a challenge. This is the real dilemma brought by gout, affecting not only the daily lives of millions but also a health issue deeply influenced by dietary habits.
Unveiling Gout: The Delicate Balance Between Purine and Health
Gout, an ancient yet prevalent disease, often hides its roots on our dining tables. When the body’s purine metabolism is imbalanced, leading to elevated uric acid levels, it could silently head towards the trap of gout. Gout is not just about joint pain; it reflects a complex biochemical process.
Research shows that high-purine foods in the diet are common triggers for gout. High-purine foods represented by red meat and seafood, if consumed excessively over the long term, significantly increase the risk of gout attacks. In contrast, the impact of purines in vegetables on gout is minimal. Some studies even suggest that moderate intake of certain vegetables can help lower uric acid levels.
It is worth noting that not everyone who consumes excessive purines will develop gout. Genetic factors, lifestyle habits, weight, and even gender play a role. For instance, obesity, hypertension, alcohol consumption can exacerbate the risk of gout.
Therefore, understanding the relationship between purines and uric acid, making sensible dietary arrangements, becomes crucial in preventing and managing gout. In practice, monitoring the purine content of food, balancing daily diets, adjusting lifestyle appropriately can effectively control blood uric acid levels, reducing the risk of gout attacks. This is the life wisdom that every gout patient needs to grasp.
Decoding the Purine Content of Foods: The Compass for Gout Diet
Gout, a disease triggered by elevated uric acid levels in the body, is closely related to the intake of purines in the diet. Controlling purine intake is crucial to managing gout.
Not all foods have the same purine content. Vegetables, fruits, and whole grains generally have low purine content, while red meat, seafood, and some alcoholic beverages have higher purine content. For example, leafy vegetables and fruits like spinach and apples have low purine content and can be consumed without worry. On the contrary, seafood like shrimp, crab, and meats like beef, lamb have higher purine content and should be eaten in moderation.
In specific figures, a medium-sized apple contains about 10 milligrams of purines, while the purine content of 100 grams of beef is approximately 110 milligrams. This comparison clearly shows the difference in purine content among different foods.
It is important to note that although some foods have high purine content, it does not mean they should be completely avoided. The key is balance and moderation. For instance, although chicken contains moderate purine content, it is safer compared to red meat. When choosing foods, gout patients should intake according to their own situation.
Another important aspect is the choice of food preparation methods. For instance, boiled vegetables may have lower purine content compared to raw ones because purines can dissolve in water, and some purines are carried away during the cooking process.
Lastly, in addition to paying attention to the purine content of foods, dietary habits are equally important. Regular meal planning, avoiding excessive hunger or overeating, ensuring adequate water intake are effective ways to help lower uric acid levels.
Gout Diet Encyclopedia – Wise Choices for a Healthy Life
Diet management for gout patients is all about balance and selection. Understanding which foods are allies and which are enemies is crucial in controlling gout attacks.
Low-Purine Foods – Safety Beacon
Foods with low purine content are safe choices for gout patients. For example, fresh vegetables like broccoli, carrots, and tomatoes not only have low purine content but are also rich in vitamins and fiber, beneficial for overall health. Whole grain foods like brown rice and whole grain bread provide necessary energy without adding purine burden. Low-fat dairy products like skim milk and low-fat yogurt can help reduce the risk of gout while supplementing calcium.
High-Purine Foods – Invisible Traps
Some foods, though delicious, are hidden traps for gout patients. Red meat, organ meats, especially shellfish and fried foods have high purine content and should be avoided as much as possible. Beer and sugary drinks are also common culprits that exacerbate gout symptoms. Take for example a 70-year-old gout patient who successfully controlled his symptoms and improved his quality of life by reducing the intake of these foods.
Fluid Intake – Eliminating Purines from the Body
Adequate fluid intake helps dilute uric acid in the blood, promoting its excretion. Drinking at least eight cups of water a day can effectively reduce the risk of gout attacks. Avoiding alcohol and sugary beverages, as they can cause dehydration and worsen gout symptoms.
Healthy Dietary Habits – Long-term Strategy
In addition to choosing the right foods, establishing healthy dietary habits is equally important. The meal timing system, i.e., eating small meals multiple times a day, helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, reducing cravings for high-purine foods. Moreover, maintaining a balanced nutrient intake, ensuring the body receives all necessary nutrients, helps control weight, reducing pressure on the joints.
Through these practical dietary management strategies, gout patients can effectively control symptoms and improve their quality of life. Remember, every small change is an important step towards a healthy life.