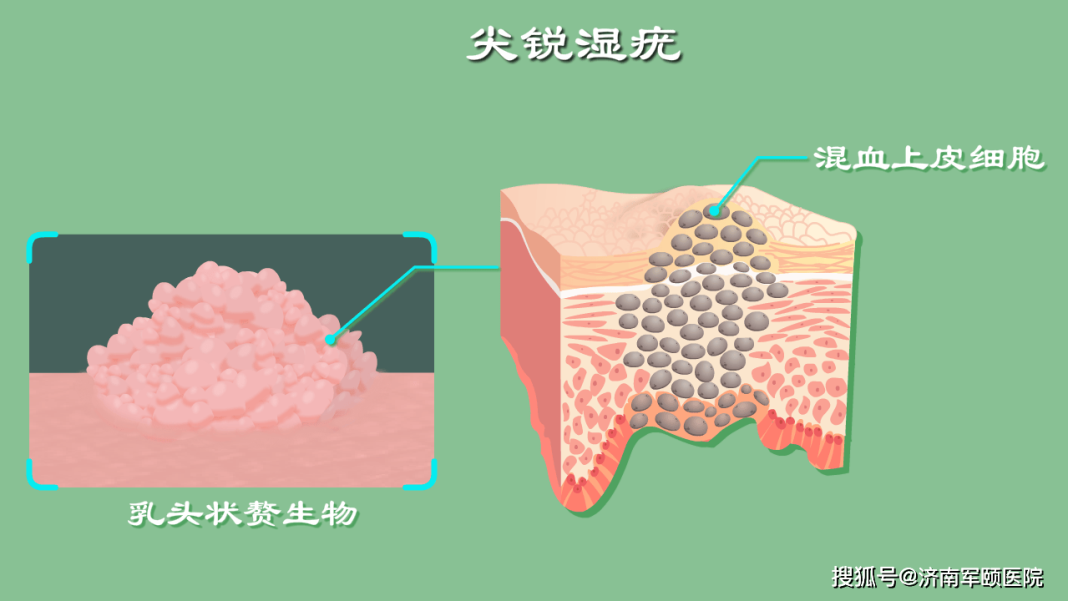
What are the consequences of HPV infection in men? Men who are infected with human papillomavirus (HPV) may experience the following outcomes:
Genital warts: The most common symptom of HPV infection is genital warts, which typically occur around the male genital area, including the **, scrotum, and other regions. After being infected with HPV, men may develop small, soft, light-colored warty lesions around the genital area or near the **, known as genital warts. This viral infection usually does not have long-term health effects, but the warty lesions may cause discomfort and itching.
Precancerous lesions: Certain high-risk HPV infections can lead to precancerous lesions in the male genital area, including ** precancerous lesions and ** precancerous lesions.
Genital cancer: Some high-risk HPV infections can increase the risk of men developing genital cancers, including ** cancer, ** cancer, and oropharyngeal cancer.
Transmission to partners: Men infected with HPV can transmit it to their partners through sexual activity, including to women. After being infected with HPV, women may develop cervical cancer or other genital cancers.
Other diseases: HPV infection may also lead to other conditions, such as genital warts, ** warts, oral warts, genital itching, pain, urethritis, and more.
Therefore, men should pay attention to sexual health, undergo regular sexually transmitted infection screenings, and get vaccinated against HPV to prevent HPV infections and related diseases. Additionally, avoiding sexual activity with multiple partners and using condoms can lower the risk of infection. Men should be aware of the risks associated with HPV infection and take preventive measures, such as using condoms, getting the HPV vaccine, and having regular health check-ups, to reduce the risk of infection. If any suspicious symptoms arise, they should seek medical attention promptly for professional diagnosis and treatment.