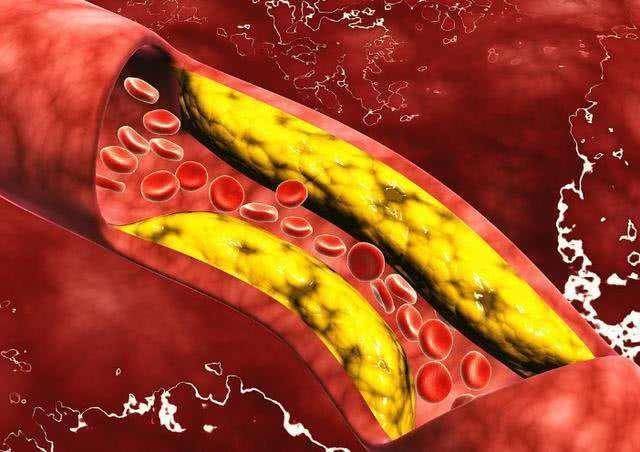
Hyperlipidemia, this medical term may sound unfamiliar, but it is a health hazard that cannot be ignored in our daily lives.
Hyperlipidemia refers to the abnormal lipid content in the blood, which is not only a potential health risk but also a potential trigger for various serious illnesses such as cardiovascular diseases and atherosclerosis.
With the acceleration of life pace, diets high in fats, sugars, and salts have gradually become mainstream, while lack of exercise, long-term sleep deprivation, and other unhealthy habits have further increased the incidence of hyperlipidemia. The presence of hyperlipidemia is like a time bomb, constantly threatening our health.
Hyperlipidemia is not without trace, as it often comes with some obvious symptoms. For example, patients may feel dizzy, fatigued, or even experience symptoms like chest tightness and shortness of breath.
These symptoms, though not fatal, silently erode our bodies, leading us unknowingly towards the abyss of disease.
Hyperlipidemia, while terrifying, is not unbeatable. As long as we take active measures, adjust our lifestyles, we can safeguard our health while enjoying a good life.
01
What is the normal blood lipid level for healthy individuals?
Blood lipids, substances in the blood mainly composed of cholesterol and triglycerides, are crucial for maintaining normal bodily functions. However, both high and low blood lipid levels can have adverse effects on health.
For healthy individuals, blood lipid levels should be within a certain range. Specifically, cholesterol is divided into high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C).
HDL-C, known as “good cholesterol,” aids in clearing cholesterol from blood vessels, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases; while LDL-C, known as “bad cholesterol,” tends to deposit on blood vessel walls, forming atherosclerotic plaques, increasing the risks of heart diseases and strokes. Therefore, maintaining high HDL-C levels and low LDL-C levels is key to maintaining healthy blood lipids.
Generally, the total cholesterol level for healthy adults should be below 200mg/dL, HDL-C level above 40mg/dL, and LDL-C level varies due to individual differences but is usually recommended to be controlled below 100mg/dL.
As for triglycerides, the normal level should be below 150mg/dL. However, these values are not fixed and may be influenced by various factors such as age, gender, genetics, diet, and lifestyle.
02
Can hyperlipidemia patients not eat cilantro?
Firstly, cilantro, as a common seasoning and ingredient, is rich in vitamins and minerals and has certain health benefits for the body.
However, for individuals with hyperlipidemia, the key lies in controlling the intake and combination. Moderate consumption of cilantro not only enhances the flavor of dishes but also helps improve appetite, contributing to enhancing the quality of life for patients.
Of course, hyperlipidemia patients should follow a low-fat, low-cholesterol diet. Therefore, when consuming cilantro, it is advisable to avoid consuming it with high-fat or high-cholesterol foods to prevent worsening the condition. In addition, patients should also pay attention to controlling total calorie intake, maintaining a balanced and diverse diet.
It is worth mentioning that in traditional Chinese medicine, cilantro has certain medicinal value. It is believed to have effects such as dispelling wind-cold, aiding digestion, and detoxification.
For hyperlipidemia patients, moderate consumption of cilantro may have a certain adjunctive therapeutic effect. However, it should be noted that this does not mean cilantro can replace medical treatments, and patients should still follow medical advice for standardized treatment.
In conclusion, hyperlipidemia patients are not completely restricted from consuming cilantro. As long as the intake and combination are controlled, moderate consumption of cilantro will not have a negative impact on the condition and may even bring some health benefits to the patients.
03
Doctor: Three types of dishes to avoid if you want to lower blood lipids
Firstly, high-fat meats should be avoided as much as possible. Meats such as fatty pork, lamb, etc., contain abundant saturated fatty acids, long-term consumption of which can increase low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in the blood, also known as “bad cholesterol,” thus worsening abnormal blood lipids.
Therefore, at the dining table, we should reduce the frequency of these high-fat meat appearances and replace them with lean meat, poultry, or fish with low fat and high protein content.
Secondly, fried foods should also be kept at a distance. Fried foods absorb a large amount of oil during cooking, turning what was originally healthy ingredients into high-fat items.
These excess oils are hard to digest in the body and eventually convert to fat deposits on blood vessel walls, leading to elevated blood lipids. Therefore, when choosing foods, avoid fried methods as much as possible and opt for healthier cooking methods like steaming, boiling, or baking.
Lastly, high-salt foods should also be consumed in moderation. Sodium ions in table salt are one of the main factors leading to increased blood pressure, which in turn is a significant factor in causing cardiovascular diseases.
Therefore, patients with hyperlipidemia should control the intake of salt, reduce the consumption of pickled foods, salty snacks, and other high-salt items to lower the risks of elevated blood lipids and blood pressure.