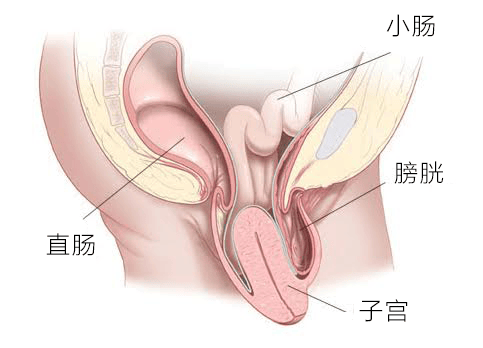
Uterine prolapse refers to the descent of the uterus from its normal position along the vagina, with the cervix protruding below the level of the ischial spines, and even completely protruding outside the vaginal opening. It is an abnormal protrusion of the uterus through the pelvic floor or genital hiatus, often accompanied by bladder prolapse, rectal prolapse, and bowel prolapse.
Activities such as square dancing can increase intra-abdominal pressure, leading to the appearance of symptoms. However, the real cause is the weakening of the supporting structures related to the pelvic organs. When the pelvic floor muscles are damaged or weakened, the uterus loses its pulling and supporting force and moves away from its original position.
The “culprit” causing ligament and pelvic floor muscle relaxation and damage
1. Pregnancy and childbirth: The more pregnancies a woman has, the higher the risk of uterine prolapse.
In particular, difficult vaginal deliveries with the assistance of forceps can lead to overstretching or tearing of the ligaments and muscles in the pelvis, weakening their strength and making it difficult to support organs. Cesarean sections also do not completely prevent the occurrence of long-term pelvic floor dysfunction disorders.
2. Poor postpartum recovery: Engaging in physical labor too soon after childbirth can also affect the recovery of pelvic floor tissues, making prolapse more likely to occur.
3. Menopause: After menopause, the decrease in estrogen levels causes the pelvic floor muscles to weaken and relax, rendering them unable to support the uterus and urinary system, making uterine prolapse more likely.
4. Prolonged increase in intra-abdominal pressure: Such as chronic coughing, constipation, abdominal obesity (apple-shaped body with waist circumference greater than hip circumference), prolonged heavy lifting, postpartum use of abdominal binders, etc.
5. Iatrogenic factors causing damage to pelvic floor support structures, such as hysterectomy and posterior colporrhaphy surgeries.
6. Muscle weakness due to connective tissue diseases or congenital abnormalities.
Mild prolapse usually presents with no symptoms.
In more severe cases, individuals may feel a “mass” protruding from the vaginal opening, along with varying degrees of pelvic heaviness, lower back pain, worsened symptoms after prolonged standing or exertion, or coughing. It may also be accompanied by urinary incontinence, difficulty urinating, constipation, discomfort during intercourse, and the “mass” may retract on its own after bed rest.
Pelvic floor reconstruction surgery treats uterine prolapse, preserving intact pelvic floor organs.
Pelvic organ prolapse resulting from pelvic floor damage and functional degradation increasingly impacts the health and quality of life of middle-aged and elderly women. Pelvic floor reconstruction surgery aims to repair female pelvic floor defects, reconstruct structures, and replace tissues to restore anatomical position of organs. It is suitable for patients requiring surgical treatment for the prolapse of pelvic floor organs (uterus, vagina, intestines, and bladder).