2021, a data statistical report on the body size of Chinese adults shows:
In 2018, there were approximately 85 million obese individuals among residents aged 18-69 in China, with men accounting for 48 million. Compared to 2004, China’s obesity rate has risen from 3.1% to 8.1%.
It is worth noting that this also indirectly reveals a fact that the obesity rate among men may be higher than women.
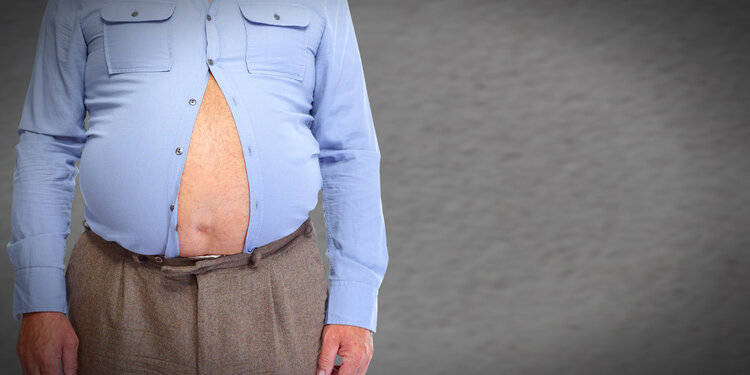
Indeed, upon closer observation, many men tend to develop a potbelly after entering middle age, raising the question of who exactly is responsible for enlarging the bellies of over 40 million men?
Who is really responsible for men’s expanding bellies?
Having a large belly in middle age seems to be an inevitable fate for men!
The “Chinese Journal of Epidemiology” once published body size data covering residents of nine provinces and regions in China, indicating that between 1993 and 2006, the average waist circumference of Chinese men aged 20-65 increased from 77.1cm to 82.9cm; while women’s waist circumference also increased by 3.1cm.
Some may wonder why men are more prone to gaining weight.
Firstly, it is closely related to physiological changes brought by aging. A study published in the top international medical journal “Nature Medicine” found that with aging, the lipid turnover rate in men significantly decreases, meaning that the rate of fat accumulation exceeds consumption. Without proper body maintenance, overweight issues are more likely to occur.
Secondly, men in middle age often face dual pressures from family and work. Under high stress, gastric secretion will be stimulated, leading to overeating and increased fat deposition rate. Additionally, prolonged sitting among middle-aged men also results in reduced physical activity, accelerating the conversion of calories into stored fat.
Defined tags here [Link] and here [Link]
Part two Heading: Bigger Belly, Higher Risk of Acute Heart Attack, from the CDC of China: The larger the belly, the higher the risk of an acute heart attack.
A bigger belly brings more illnesses.
A study conducted by the China CDC analyzed data from 26,794 residents on chronic diseases and risk factors. The study found that individuals with a body mass index (BMI) <24 but with a larger waist circumference than normal have an 85% increased risk of acute heart attacks; individuals with a BMI of ≥24 and a waist circumference exceeding the normal standards have a 56% higher risk of acute heart attacks. Furthermore, individuals with a normal waist circumference, even with a BMI of ≥24, do not have an increased risk of acute heart attacks.
Therefore, a larger belly may be associated with a higher incidence of diseases. Moreover, as organs like the liver, pancreas, and gastrointestinal tract are concentrated in the abdominal cavity, when a large amount of fat accumulates in the abdomen, the surrounding and internal areas of these organs are also covered with a significant amount of fat, leading to the development of fatty liver. Additionally, overweight and obese individuals with an enlarged waist circumference are at a higher risk of insulin resistance, making them 2-5 times more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than normal individuals.
Heading three: These 4 Symptoms Indicate Cancer
Don't underestimate a big belly, as it not only affects one's appearance but also reflects their physical health.
1. Presence of a lump:
If an abnormal lump suddenly appears in the abdomen, excluding traumatic factors, and rapidly increases in size within a short period, with a hard texture, unclear boundaries, and difficult to move, this could potentially indicate a tumor. For instance, colon cancer can lead to a hard lump in the abdomen.
2. Unexplained pain:
Sudden abdominal pain, dull pain, stabbing pain, or pulling pain that cannot be relieved by normal medication and lasts for a long duration should be carefully observed for the possibility of cancer. For example, gastric cancer often presents with upper abdominal pain, accompanied by nausea, weight loss, and digestive discomfort. Additionally, liver cancer can cause abnormal abdominal pain, primarily focused in the right upper abdomen, leading to severe colic-like pain.
3. Sudden increase in waist circumference:
A rapid increase in waist circumference over a short period may not just be due to obesity but could be a sign of ascites. The progression of cancer can also manifest with similar symptoms, mainly arising from abnormal manifestations caused by cancer cells extending towards the peritoneum. Common types of cancer include lung cancer, liver cancer, pancreatic cancer, ovarian cancer, and colon cancer.
4. Prominent veins:
Due to the higher fat content in the abdominal wall, visible veins are not easily noticeable. However, the compression of blood vessels resulting from tumor pressure on organs in the abdominal cavity or conditions like ascites and liver cirrhosis can lead to restricted venous blood return, causing significant vein dilation, appearing as prominent veins.
Heading four: Revealing Longevity Through the Belly Button
In reality, there are many physical indicators of lifespan, one of which is the belly button. If someone's belly button exhibits these 3 characteristics, it may signify longevity.
1. Warm Belly Button:
The temperature of the belly button reflects one's bodily condition. Those with a slightly lower belly button temperature often feel cold in the abdomen, indicating weakness in the spleen and stomach. Conversely, individuals with a well-tempered belly button tend to have sufficient qi and blood circulation, normal body functions, lower disease incidence, and a higher probability of longevity.
2. Moderate Position of the Belly Button:
The position of the belly button also reflects one's body type; individuals with a centrally positioned belly button indicate proper body management without risk factors of being underweight or overweight. Additionally, the belly button plays a role in improving blood circulation and organ function, making individuals with a centrally positioned belly button generally healthier and potentially living longer lives.
3. Clearly Indented Belly Button:
Traditional Chinese medicine views a concave belly button as a sign of a healthy spleen and stomach. This indicates that with healthy spleen and stomach development, nutritional needs can be better met, displaying a more robust vitality in the body.
In conclusion, abdominal issues are closely linked to health, and should not be taken lightly. The changes in the abdomen due to being underweight or overweight may not have immediate effects, but over time can pose health risks. Therefore, it is essential to control diet and increase exercise to prevent the occurrence of the mentioned abnormal abdominal manifestations!