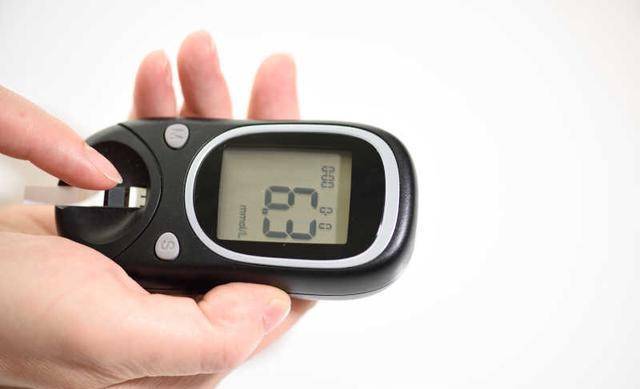
Introduction: Diabetes, this term is not unfamiliar to people in their daily lives, it is known as the “undying cancer,” indicating that once contracted, it requires long-term adjustments and control in diet, lifestyle habits, and medication treatment.
The main cause of diabetes is an error in the regulation of sugar in the body, leading to the inability of sugar to be normally converted, resulting in the accumulation of sugar in the blood, manifested by abnormal elevation and fluctuation of blood sugar.
Once diabetes exists, not only is it necessary to control blood sugar levels through medication or insulin, but dietary regulation for diabetes is an important means of treatment.
Patients need to adjust their diet structure in a timely manner, increase the intake of foods that help lower blood sugar, which is of great significance for the stability and control of the condition.
Many foods can achieve a natural hypoglycemic effect, and some foods can even be called natural “insulin.” Eating them regularly in daily life may help avoid the dangers of diabetes.
Polyuria (frequent urination): Elevated blood sugar levels in diabetes patients require the kidneys to work harder to filter out excess sugar, leading to frequent urination; thirst and dry mouth: Due to frequent urination, the body loses a large amount of water, causing thirst and dry mouth; increased hunger: Due to the body’s inability to effectively use glucose in the blood, resulting in insufficient energy, leading to increased hunger;
Blurred vision: High blood sugar levels may cause eye disorders, resulting in blurred vision or changes in vision.
Individuals with a family history: People with a family history of diabetes are more likely to develop diabetes, genetic factors play an important role in the onset of diabetes.
Obese or overweight individuals: Obesity and overweight are major risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes.
Individuals with a lack of physical activity: Lack of physical activity increases the risk of developing diabetes. Exercise can help control weight, improve insulin sensitivity, and prevent diabetes.
Elderly individuals: With age, the risk of diabetes increases. Middle-aged and elderly individuals are more susceptible to diabetes.
Individuals with hypertension: Hypertension is closely related to diabetes. Individuals with hypertension are more likely to develop diabetes.
Individuals with high cholesterol levels: High cholesterol levels may increase the risk of developing diabetes.
Individuals with unhealthy dietary habits: High-sugar, high-fat, high-salt, and low-fiber diets can lead to obesity and high blood sugar.
Tomatoes are a food rich in various nutrients, including a variety of vitamins. For diabetes patients, consuming tomatoes in moderation can enhance immunity and disease resistance.
Tomatoes contain a certain substance called lycopene, which can effectively inhibit vascular activity, thereby reducing the development of atherosclerosis and some aspects of diabetes.
However, if a patient’s blood sugar control is unstable, eating tomatoes may not lower blood sugar. So, when choosing to eat tomatoes, it is necessary to moderate intake based on one’s own conditions.
In addition, below are some natural insulin-like foods that are quite common in daily life, and eating more of them may help us stay away from the harm of diabetes:
Okra
Okra has been popular in recent years as a stomach-nourishing vegetable, containing a certain amount of mucin protein that can effectively nourish the stomach and kidneys. Regular consumption of okra can also possess certain nutrients that can lower blood sugar levels. Okra contains a certain amount of quercetin, which can effectively block the absorption of sugar and starch in the body, thus aiding in auxiliary hypoglycemic effects.
Okra also contains a certain amount of dietary fiber, which can block the absorption of sugar and fats in the body, help enhance metabolism, not only for weight loss but also effectively reduce the occurrence of diabetes problems.
Mulberry
Mulberry is a delicious fruit, not only sweet and sour, but also rich in various vitamins and antioxidants. These antioxidants can help slow down the rise in blood sugar, promote the action of insulin, thereby helping to lower blood sugar levels.
Mulberries are rich in vitamin C, vitamin E, vitamin K, and vitamin B group. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that can reduce the production of free radicals and protect cells from damage.
The hypoglycemic effect of mulberries is most prominent, studies have shown that the polysaccharides, flavonoids, and alkaloids in mulberries can significantly lower blood sugar levels, improving blood sugar control in diabetes patients.
Purslane
Purslane is a common wild vegetable in daily life, rich in nutrients, not only in dietary fiber, but also in vitamin C, carotene, B vitamins, calcium, iron, phosphorus, and other nutrients.
Purslane is rich in a certain adrenaline component that can effectively regulate glucose metabolism in the body, help promote pancreatic insulin secretion, thereby stabilizing blood sugar levels.
For individuals with high blood sugar levels, appropriately regulating their diet can not only assist in lowering blood sugar but also help reduce blood viscosity, thereby helping prevent cardiovascular diseases.
Salmon
Salmon, a nutritious delicacy, its value far exceeds its delicious taste, this seafood rich in Omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D play important roles in human health.
The Omega-3 fatty acids in salmon help improve cardiovascular health, lower cholesterol and triglyceride levels, reducing the risk of heart disease.
In addition, Omega-3 fatty acids can promote insulin function, allowing the body to more effectively utilize blood sugar, helping to control blood sugar levels, especially beneficial for diabetes patients.
Cardiovascular Diseases
The impact of high blood sugar on the cardiovascular system is most pronounced; long-term high blood sugar damages blood vessel walls, increases the risk of atherosclerosis, heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular diseases. Nervous System Disorders
High blood sugar damages nerve cells, leading to peripheral neuropathy (such as diabetic peripheral neuropathy) and autonomic neuropathy (such as diabetic autonomic neuropathy), which can cause sensory abnormalities, motor disorders, autonomic dysfunction, etc.
Kidney Diseases
Long-term high blood sugar can damage the small blood vessels and glomeruli of the kidneys, leading to the development of diabetic nephropathy, one of the main causes of chronic kidney disease. Eye Diseases
Diabetes can cause eye disorders, including diabetic retinopathy (leading to visual impairment) and diabetic cataracts (forming opaque crystalline lenses).
Exercise
Moderate aerobic exercise can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Choose suitable exercise methods such as walking, running, swimming, cycling, etc.
Engage in at least 150 minutes of aerobic exercise per week, combined with strength training to increase muscle mass and metabolism.
Maintain Good Sleep
Poor sleep can lead to hormonal imbalance, disrupt insulin secretion and utilization. Establish good sleep habits, maintain sufficient sleep time, avoid excessive fatigue and stressful living conditions, to help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Follow Medical Advice for Rational Medication Use
In some cases, diet and exercise may not meet the needs of blood sugar control, and doctors may prescribe medication treatment.
Drug treatment includes oral medications and insulin injections, can help control blood sugar levels. During drug treatment, strictly adhere to the doctor’s medication guidance, monitor blood sugar regularly, and adjust medication dosage in a timely manner.