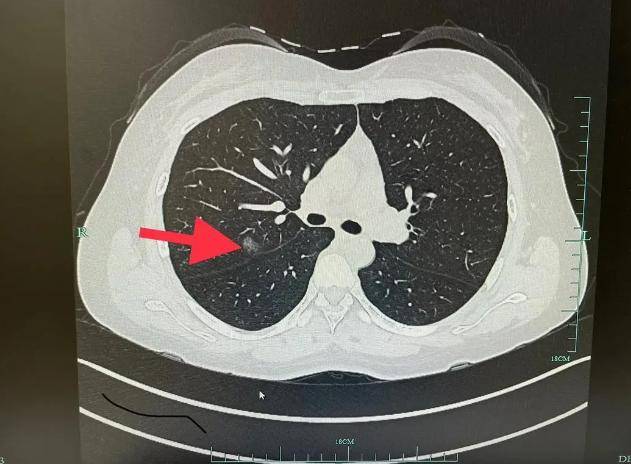
Pulmonary nodules, though may sound somewhat unfamiliar, are not as rare as we might imagine in real life. In many medical examination reports, the appearance frequency of pulmonary nodules is quite common. Although most pulmonary nodules are benign, there is still a risk of some nodules evolving into lung cancer.
Facing this situation, how to effectively prevent and manage pulmonary nodules has become a focus of attention for many people. In this process, the role of diet cannot be ignored.
This article will delve into the four “pathogenic factors” that people with pulmonary nodules should avoid in their diet, and explain in detail why resisting these foods may help nodules dissipate.
Unveiling Pathogenic Factors: Revealing Their Definitions, Types, and Effects
In traditional Chinese medicine theory, pathogenic factors refer to foods that have stimulating properties, easily lead to diseases, or worsen the condition. This article will provide you with a detailed introduction to the definition, types, and effects of pathogenic factors on bodily health, helping you better understand and guard against the risks posed by pathogenic factors.
I. Definition of Pathogenic Factors
Pathogenic factors, as the name suggests, refer to foods that can induce or worsen certain diseases or symptoms. In traditional Chinese medicine theory, foods are categorized into four natures: cold, hot, warm, and cool, and pathogenic factors typically belong to hot foods. Consuming pathogenic factors may cause symptoms like fever, inflammation, allergies, and in severe cases, worsen conditions.
II. Types of Pathogenic Factors
1. Pathogenic Factors in Meat
(1) Lamb: Lamb is warm in nature, with the effects of tonifying deficiency, strengthening yang, and warming the stomach. However, excessive consumption of lamb may lead to body heat and exacerbate inflammation.
(2) Dog meat: Dog meat is hot in nature, having a warming effect. However, excessive consumption may lead to increased blood pressure and worsen heart disease.
(3) Chicken: Chicken is warm in nature with nourishing effects. However, individuals with symptoms like colds and coughs may worsen their condition by consuming chicken.
2. Pathogenic Factors in Vegetables
(1) Green onion, ginger, garlic: Green onion, ginger, and garlic have the effects of warming the middle and dispersing cold, inducing sweating, and releasing the exterior. However, excessive consumption can lead to symptoms like stomach heat and oral ulcers.
(2) Chili pepper: Chili pepper is hot in nature with stimulating properties. Individuals with gastritis, gastric ulcers, etc., should avoid consuming chili peppers.
(3) Spinach: Spinach is warm in nature with blood-nourishing effects. However, individuals with rheumatoid arthritis may worsen their condition by consuming spinach.
3. Pathogenic Factors in Fruits
(1) Durian: Durian is hot in nature with nourishing effects. However, individuals with diseases like diabetes, hypertension, etc., should consume durian with caution.
(2) Mango: Mango is warm in nature with intestinal moistening and laxative effects. However, individuals with allergic constitutions may experience skin allergies if they consume mango.
4. Other Pathogenic Factors
(1) Alcohol: Alcohol has stimulating properties, excessive drinking may lead to diseases like gastritis and gastric ulcers.
(2) Coffee: Coffee has refreshing effects, but excessive consumption may lead to symptoms like insomnia and palpitations.
III. Effects of Pathogenic Factors on Bodily Health
1. Fever: Consuming pathogenic factors may lead to body heat, worsening the condition.
2. Inflammation: Certain components in pathogenic factors may exacerbate inflammation, affecting disease recovery.
3. Allergies: Some pathogenic factors may cause allergic reactions, such as skin allergies, asthma, etc.
4. Indigestion: The stimulating components in pathogenic factors may affect the digestive system, leading to symptoms like indigestion, diarrhea, etc.
Unveiling the Mystery of the Lungs: What Are Pulmonary Nodules?
In the medical field, pulmonary nodules are a common pulmonary lesion, but for many people, it remains a relatively unfamiliar term. This article will elaborate on what pulmonary nodules are, as well as their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment methods, revealing the mysterious veil of the lungs together.
I. What Are Pulmonary Nodules?
Pulmonary nodules refer to localized parenchymal lesions with a diameter less than 3 cm formed within the lung parenchyma. They can be single or multiple, and based on the nature of the lesion, can be classified as benign nodules and malignant nodules. Benign nodules include inflammations, tuberculosis, hamartomas, etc., while malignant nodules, primary lung cancer is the most common.
II. Causes of Pulmonary Nodules
1. Infection: Pathogens like bacteria, viruses, fungi infect the lungs, causing localized inflammatory reactions and forming pulmonary nodules.
2. Benign tumors: Such as hamartomas, pulmonary alveolar cell tumors, etc., these tumors form pulmonary nodules during their growth process.
3. Malignant tumors: Such as primary lung cancer, metastatic lung cancer, tumor cells in the lungs form nodules.
4. Genetic factors: Certain genetic diseases like tuberous sclerosis, pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis, can lead to the formation of pulmonary nodules.
5. Immunological diseases: Such as sarcoidosis, granulomatous lesions, abnormal immune system leading to nodules in the lungs.
III. Symptoms of Pulmonary Nodules
In the early stages, pulmonary nodules often have no obvious symptoms, and many patients discover them incidentally during examinations. As the nodules increase in size, some patients may experience the following symptoms:
1. Cough: Irritative dry cough or with phlegm.
2. Hemoptysis: Bloody or slight hemoptysis in sputum.
3. Chest pain: Enlarged nodules compress surrounding tissues, causing chest pain.
4. Dyspnea: Nodules obstructing the bronchus, leading to breathing difficulties.
5. Fever: Infectious pulmonary nodules can cause fever.
Patients with pulmonary nodules should refrain from eating: a list of four major “pathogenic factors”, resisting the urge to eat, and assisting in maintaining good health
I. List of Four Major “Pathogenic Factors”
1. Seafood: such as shrimp, crab, shellfish, etc.
Seafood is rich in protein and trace elements, but the heterologous protein in it is prone to causing allergies, leading to inflammatory reactions. For patients with pulmonary nodules, consuming seafood may stimulate nodule growth and worsen the condition.
2. Lamb: Lamb is warm in nature, with the functions of tonifying qi and nourishing blood. However, overconsumption may lead to excessive internal heat and worsen inflammation. For patients with pulmonary nodules, the heterologous protein in lamb may also stimulate nodule growth.
3. Spicy foods: such as chili peppers, ginger, garlic, etc.
Spicy foods have strong irritative properties and are likely to cause internal heat and worsen inflammation. Consuming spicy foods for patients with pulmonary nodules may exacerbate nodule symptoms, hindering their recovery.
4. Pickled foods: such as cured meat, pickled vegetables, etc.
Pickled foods contain a high amount of nitrites, prolonged consumption may increase free radicals in the body, stimulating nodule growth. Additionally, the high salt content in pickled foods may lead to edema, worsening the condition.
II. Why restraining from eating is winning?
1. Avoid stimulating nodule growth: Patients with pulmonary nodules should try to consume fewer of the four major “pathogenic factors” mentioned above, as the heterologous proteins and spicy components in these foods may stimulate nodule growth and worsen the condition.
2. Reduce inflammatory reactions: Patients with pulmonary nodules often have inflammatory reactions. Consuming “pathogenic factors” may exacerbate inflammation, affecting disease recovery. Resisting the urge to eat helps reduce inflammatory reactions.
3. Boost immunity: A balanced diet helps boost immunity, enhancing the body’s resistance. Avoiding “pathogenic factors” is advantageous for patients with pulmonary nodules to maintain good physical condition.
4. Promote disease recovery: Refraining from eating the four major “pathogenic factors” helps in the recovery of patients with pulmonary nodules. Alongside dietary adjustments, cooperating with medical treatment aids in faster recovery.
III. How to eat correctly?
1. Maintain a balanced diet: Patients with pulmonary nodules should ensure a diverse diet, intake adequate protein, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals.
2. Consume fresh fruits and vegetables in moderation: Fresh fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins and antioxidants, helpful in boosting immunity and promoting disease recovery.
3. Pay attention to cooking methods: Opt for cooking methods like steaming, stewing to avoid high-calorie, high-fat techniques like deep-frying, grilling.
4. Regular check-ups: Patients with pulmonary nodules should undergo regular follow-ups, closely monitor changes in their condition, and adjust their diet promptly.
In conclusion, individuals with pulmonary nodules should consume the four major “pathogenic factors” as little as possible, resisting the urge to eat is winning. Through a sensible diet, maintaining good physical condition, aiding in disease recovery. Simultaneously, actively complying with medical treatment, following doctor’s advice, can effectively overcome illnesses and regain health.