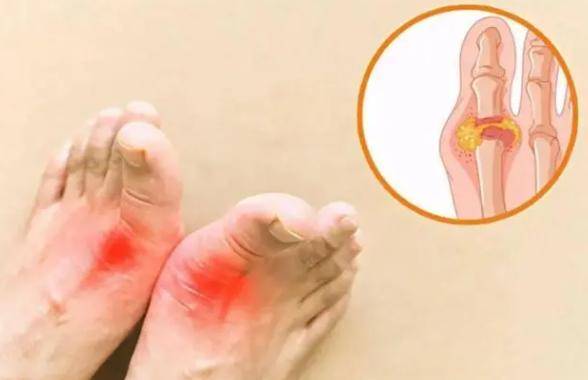
Purine, mainly in the form of purine nucleotides, plays a very important role in energy supply, metabolic regulation, and the composition of coenzymes. Purines are present in the cell nucleus and are the basic components of all living cell organisms. In the human body, purines are oxidized to form uric acid, and high uric acid levels can lead to gout.
Dietary purines are classified into 4 levels: very high, high, moderate, and low purine foods. The amount of purine intake largely determines the production of uric acid.
The “new standard” for uric acid levels has been revealed, with different values for males and females! According to the 2022 uric acid standard, the uric acid value for males ranges between 237.9-356.9 moles per liter, while for females, it ranges from 178.4-297.4 moles per liter, indicating that females generally have lower uric acid levels. Uric acid levels also have a fluctuation range, and being within a reasonable fluctuation range indicates good health.
If the uric acid value exceeds 360 for females or is above 420 for males, it indicates high uric acid levels, while exceeding 540 is a sign of very high uric acid levels and requires attention.
Can seafood lead to high uric acid levels? Seafood is a high-purine food, and consuming excessive amounts can increase purine intake, leading to elevated uric acid levels, which is linked to certain health risks that patients need to be aware of.
Natural “purine king,” which is five times higher in purines than seafood, should be consumed in moderation, according to doctors.
1. Fungi:
Fungi have always been an important part of people’s diets, rich in protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, beneficial for health. However, research shows that fungi have relatively high purine content, with mushrooms containing up to 150mg/100g of purines, categorizing them as high-purine foods.
For individuals with high uric acid levels, limiting purine intake is crucial, and since mushrooms have high purine content, patients should avoid them as much as possible.
2. Bamboo Shoots:
Bamboo shoots, despite their high nutritional value, also have high purine content, especially during the spring season when purine content is higher. Therefore, individuals with high uric acid or gout should consume bamboo shoots in moderation.
3. Bean Sprouts:
Soybean-based foods are rich in purines, and bean sprouts are derived from soybeans or mung beans without significant processing, retaining their purine content. It is not suitable for individuals with high uric acid levels to consume bean sprouts in excess, as it may trigger gout.
4. Cruciferous Vegetables:
Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower are rich in vitamins and essential micronutrients, promoting anticancer and antioxidative effects. However, their high purine content makes them unsuitable for individuals with high uric acid levels.
5. Spinach:
Spinach is rich in iron, commonly consumed to address anemia or blood deficiency. However, its high purine and oxalic acid content can impact digestion and metabolism efficiency, leading to increased uric acid levels.
6. Knotweed:
Knotweed is rich in nutrients such as vitamin C, beta-carotene, vitamin A, and potassium, with low fat content, aiding weight loss. However, its high purine content makes it unsuitable for individuals with high uric acid levels, as it can worsen gout.
When uric acid levels are elevated, engaging in regular exercise, adjusting diet appropriately, staying hydrated, and timely medication intake are crucial for preventing health risks associated with high uric acid levels.