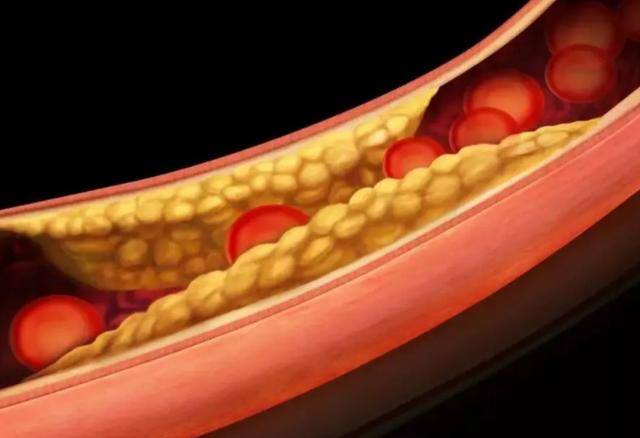
Introduction: Hyperlipidemia, as a common term in daily conversations, is more accurately described as “lipid abnormality.” This is a pathological condition describing an imbalance in lipid levels in the blood.
Specifically, when the levels of cholesterol (CH), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in our serum exceed normal ranges, or when triglycerides (TG) levels increase, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels decrease, we can refer to it as hyperlipidemia or lipid abnormality.
Lipids in plasma do not exist independently but are transported in the form of lipoproteins in the blood. Abnormalities in lipoproteins can lead to hyperlipidemia, commonly known as hyperlipidemia. These lipoproteins include the well-known LDL and HDL, and their metabolism and balance in the body are crucial for maintaining health.
Hyperlipidemia is not just a seemingly common health issue; its potential risks should not be underestimated. Prolonged lipid abnormalities can easily lead to atherosclerosis-related cardiovascular diseases, such as coronary heart disease, stroke, and more. Once these diseases occur, they can have serious effects on the patient’s health and quality of life.
Additionally, recent studies have also found a certain correlation between lipid abnormalities and the risk of tumors, making the prevention and treatment of hyperlipidemia particularly important.
What are the normal values of blood lipids?
The normal values of blood lipids vary depending on individual constitution, age, gender, dietary habits, and other factors. However, generally, we can understand the normal range of blood lipids based on some common medical reference values.
Total Cholesterol (TC)
The total cholesterol level in normal individuals should be below 200mg/dL. However, this value is not absolute because some individuals may have slightly high total cholesterol levels but may not pose a high cardiovascular risk due to higher levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL)
Low-density lipoprotein is the main lipid that leads to atherosclerosis; thus, the lower the level, the better. The LDL level in normal individuals should be below 100mg/dL, but some individuals may need even lower levels, especially those with existing cardiovascular diseases or high risk.
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL)
High-density lipoprotein is a beneficial lipid that helps the body clear excess cholesterol. Therefore, the higher the HDL level, the better. The HDL level in normal individuals should be above 40mg/dL, with an ideal HDL level should be above 60mg/dL.
Triglycerides (TG)
Triglycerides are another common lipid in the blood. Although they play an important role in the body, high levels of triglycerides increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases. The normal level of triglycerides in individuals should be below 150mg/dL.
What are the causes of hyperlipidemia?
Lack of exercise
The fast pace of modern life leads many individuals to lack sufficient exercise time due to busy work schedules or life stress. Prolonged lack of exercise can slow down the body’s metabolism, causing lipids in the blood to accumulate due to ineffective consumption and utilization, resulting in hyperlipidemia.
Excessive mental stress
Prolonged mental stress keeps the body’s stress response continually activated, leading to increased secretion of hormones like adrenaline, which promotes fat synthesis and storage, raising lipid levels in the blood.
Chronic diseases
Conditions like diabetes, hypothyroidism, and others can also lead to high blood lipids. These diseases affect the body’s metabolism, hindering proper lipid metabolism and excretion, resulting in hyperlipidemia.
Some medications
Drugs such as diuretics, glucocorticoids, and others may also cause hyperlipidemia. These medications interfere with the body’s lipid metabolism, resulting in increased lipid levels in the blood.
Is walking helpful in lowering blood lipids?
In recent years, with increasing health awareness, people have begun paying more attention to maintaining and improving their health through daily activities. Walking, as a simple, easy, and equipment-free exercise, has become popular among the general public. And more scientific research confirms that walking has a significant positive effect on lowering blood lipids.
So why is walking helpful in lowering blood lipids? Firstly, walking as an aerobic exercise effectively promotes the body’s metabolism. During walking, the body needs to consume energy mainly derived from the breakdown of fats and sugars.
Through continuous aerobic exercises like walking, the body can efficiently break down and consume fats, reducing blood lipid levels. Secondly, walking can also improve the body’s endocrine function, promoting lipid metabolism and excretion.
During walking, the body secretes beneficial hormones and enzymes that play crucial roles in lipid metabolism. They promote fat breakdown and oxidation, accelerate lipid transport and excretion, and reduce lipid accumulation in the body.
Furthermore, walking helps improve blood circulation. Good blood circulation ensures timely delivery of lipid substances to metabolic organs like the liver for metabolism and excretion. Through walking, we can enhance cardiovascular function, increase blood flow rate, thus aiding in lowering blood lipid levels.
Specific research data also support this conclusion. For example, a study published in a reputable medical journal pointed out that individuals who engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, such as walking, per week, have significantly lower blood lipid levels than those who do not exercise regularly.
Another study targeting middle-aged individuals found that long-term adherence to walking can effectively lower total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels while increasing HDL cholesterol levels. These research findings fully demonstrate the positive effects of walking on lowering blood lipids.
Of course, to achieve the effect of lowering blood lipids through walking, we also need to note the following:
Maintain appropriate walking time and intensity, gradually increase exercise according to individual conditions;
Consistently engage in long-term exercise without sporadic activity;
Coordinate with a balanced diet and lifestyle habits to collectively maintain cardiovascular health.
In conclusion, walking is a simple and effective method to lower blood lipids. By increasing the time and intensity of walking, we can effectively promote fat consumption and metabolism, lower blood lipid levels, thereby maintaining cardiovascular health. Let’s start engaging in outdoor activities now and enjoy the health and happiness from walking!
Doctor’s suggestion: Eating specific foods daily is more effective in lowering blood lipids than walking
Oats
Oats, as a nutritious grain, not only have a unique taste but also contain various beneficial components for blood lipids, making them an ideal food for individuals with hyperlipidemia.
Oats are rich in soluble dietary fiber, especially beta-glucans. This soluble dietary fiber can bind with cholesterol in the intestines, forming complexes that are not easily absorbed, reducing cholesterol absorption and further lowering cholesterol levels in the blood. Scientific research has shown that individuals who consume oats regularly tend to have lower cholesterol levels in their blood.
Oats also have a relatively high content of unsaturated fatty acids. These unsaturated fatty acids can lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels in the blood, and LDL-C is a major risk factor for atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, increasing oat intake helps improve blood lipid levels, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Wax gourd
Eating more wax gourd can help lower blood lipids, a view widely accepted in modern nutrition and traditional Chinese medicine theories. Wax gourd, a common summer vegetable, not only has a refreshing taste but also contains a variety of nutrients that significantly aid in lowering blood lipids.
Wax gourd has an extremely low fat content, almost negligible. For individuals with hyperlipidemia, choosing low-fat foods is one of the important measures for controlling blood lipid levels. The low-fat characteristic of wax gourd makes it an ideal ingredient for lowering blood lipids.
Additionally, wax gourd is rich in dietary fiber, especially soluble dietary fiber. These dietary fibers can bind with cholesterol in the intestines, forming complexes that are not easily absorbed, reducing cholesterol absorption and further lowering cholesterol levels in the blood. Dietary fiber also promotes intestinal motility, aiding digestion and excretion, reducing fat accumulation in the body.
Celery
In the pursuit of a healthy diet, people are increasingly concerned about the impact of food on blood lipid levels. Celery, as a common and nutritious vegetable, has gradually been recognized for its positive effects on lowering blood lipids.
Celery is rich in dietary fiber, which has a significant effect on reducing blood lipid levels. Dietary fiber can bind with cholesterol and triglycerides in the intestines, forming substances that are not easily absorbed by the intestines, reducing the absorption and accumulation of these lipids in the body. Therefore, eating more celery helps lower cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the blood, improving blood lipid conditions.
Furthermore, celery contains various vitamins and minerals that have a positive effect on lowering blood lipids. For example, celery is rich in vitamins C and E, both of which are antioxidants that can eliminate free radicals in the body, reduce oxidative stress, protect the cardiovascular system from damage. In addition, celery is also rich in potassium, magnesium, and other minerals, which help maintain the normal function of the cardiovascular system, reduce blood pressure, further promote lipid metabolism and excretion.
Tomato
Tomato, as a common vegetable, not only has vibrant color, delicious sweet and sour taste but also contains various nutrients that have significant effects on lowering blood lipids.
Tomatoes are rich in lycopene, a potent antioxidant. It can eliminate free radicals in the body, reduce oxidative stress on the cardiovascular system, helping protect cardiovascular health. Studies have shown that lycopene can lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels in the blood and increase high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels, thereby aiding in lowering blood lipids.
In addition, tomatoes are rich in dietary fiber, especially soluble dietary fiber. This fiber can bind with cholesterol in the intestines, forming complexes that are not easily absorbed, reducing cholesterol absorption and lowering blood cholesterol levels. Furthermore, dietary fiber promotes intestinal motility, aiding digestion and excretion, reducing fat accumulation in the body.
The hazards of high blood lipids in the body: don’t underestimate the following 5 threats.
Inducing coronary heart disease
This is because lipids in the blood deposit on the blood vessel walls, gradually forming plaques that narrow the blood vessels, leading to insufficient blood supply to the heart. When this inadequate blood supply progresses to a certain extent, it can trigger severe symptoms of coronary heart disease such as angina and myocardial infarction.
Causing stroke
Stroke is a serious cerebrovascular disease, including ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke. People with high blood lipids are at higher risk of atherosclerosis due to lipid deposition in the blood vessel walls, increasing the risk of stroke.
Accelerating the progression of atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a systemic disease that not only affects the heart and brain but also affects the body’s vascular system. Individuals with high blood lipids, due to excessive lipids in the blood, accelerate the progression of atherosclerosis, causing systemic vascular changes.
Inducing fatty liver
The liver is an essential organ in the body with detoxification and metabolic functions. When blood lipids are high, a large amount of fat accumulates in the liver, causing fatty liver. If not promptly treated, fatty liver can further develop into severe diseases like cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Damaging the kidneys
The kidneys are the body’s excretory organs responsible for eliminating waste and toxins from the body. Individuals with high blood lipids, due to excessive lipids in the blood, are prone to lipid glomerulosclerosis, leading to impaired kidney function. Prolonged hyperlipidemia may also cause renal artery sclerosis, further worsening kidney damage.
End of Translation